Emergency rooms play a critical role in the U.S. healthcare system, providing immediate care to those needing urgent medical attention. For many, the ER is their only access to medical treatment, whether for economic reasons, systemic barriers to care, or the nature of their condition. As such a vital pillar to the infrastructure of the American health network, it’s no surprise that some hospitals see hundreds of thousands of patients a year.
While hospitals continuously strive to provide the best patient care, not all hospitals are equipped to handle such high numbers. For this reason, it’s important to investigate the causes and potential risks of emergency rooms with high volumes of patients. In this report from NY Requirements, we’ve compiled a list of the 25 hospitals across the country that see the most ER visits to get a closer look at the matter.
Why Some ERs See More Patients
Location is one of the primary reasons some hospitals see more ER visits. Hospitals in big cities or that serve a larger population will have more accidents and medical emergencies requiring immediate attention. Cities also tend to have higher rates of homelessness and poverty, which leads to more people using the ER as their main source of healthcare. These individuals often don’t have health insurance or a primary doctor, meaning they have nowhere else to go when they get sick. A report from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality states that uninsured patients are three times more likely to use ERs than their insured counterparts.
Additionally, that same report found uninsured patients more likely to be sick. Because these patients don’t have access to primary care services, they are forced to resort to emergency services when their conditions worsen. Parkland Health and Hospital System, which sees the most ER visits of any hospital in the country, is located in the highly populated Dallas County, in a state with some of the nation’s worst health insurance rates. While this hospital has been lauded for its efficiency in treating its high number of patients, it has also received criticism for its insufficient safety measures.
The Risks of Overcrowded Emergency Rooms
While any hospital servicing a large population should be lauded for the many lives it saves, hospitals that don’t have the proper resources to meet demand pose a significant risk to patients. One review found that overcrowded emergency departments increase wait times even for patients in critical condition, resulting in treatment delays, which can increase mortality by up to 16%.
The report also found that overcrowded hospitals are more likely to result in medical errors. Overcrowding puts significant pressure on healthcare workers, and when doctors and nurses are dealing with too many patients at once, they can become overwhelmed and make fatal mistakes. Additionally, ER staff are more likely to experience burnout when constantly dealing with high patient volumes, leading to more stress and fatigue.
Another significant risk is that overcrowding can stretch hospital resources thin. If there aren’t enough hospital beds, equipment, or staff available, it can reduce the overall quality of care. In extreme cases, patients and ambulances may need to be diverted to other hospitals, which can delay critical care and put lives at risk. At Yale New Haven Health, which ranked 5th on our list, patients have even been forced to stay in beds in the hallway.
The Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act (EMTALA)
One important law that affects emergency room visits is the Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act or EMTALA. This law requires hospitals to treat anyone who comes to the ER, regardless of whether they have insurance or can pay for the care. No matter their condition, the hospital must provide treatment until the patient is stabilized or transferred.
While EMTALA helps ensure that everyone gets emergency care, it also means that people who might not otherwise be able to get treatment—like the uninsured or underinsured—are more likely to use the ER. This can lead to higher numbers of patients and more strain on hospital resources, which is one of the reasons why hospitals in areas with larger uninsured populations tend to have the busiest ERs.
What Can Be Done to Decrease Risk of ER Overcrowding?
There’s no simple solution to fixing overcrowded emergency rooms, but there are steps that could help reduce the strain. One of the biggest changes needed is improving access to primary care. People with regular access to a doctor can get help before their health problems become emergencies.
Hospitals can invest in expanding their facilities to increase bed capacity or to handle less severe cases, similar to the expansion done by Lakeland Regional in 2015. These centers are designed to treat conditions that aren’t life-threatening, which would free up emergency rooms to handle true emergencies.
Addressing hospital staffing shortages is also critical, as emergency rooms need more doctors, nurses, and medical support staff to meet demand. This would not only improve patient care but also help reduce wait times and prevent healthcare workers from burning out.
Conclusion
The high number of ER visits at some U.S. hospitals comes from a combination of factors, from location and population size to deeper issues in the healthcare system. The risks of crowded emergency rooms are serious, but improving access to healthcare, creating more outpatient options, and addressing staffing challenges can all help reduce the number of patients flooding ERs and enhance the quality of care for everyone involved.
As the demand for emergency rooms continues to rise, healthcare professionals must stay informed and compliant with ever-changing industry regulations. If you're a medical professional or administrator in New York, ensure you're meeting your state's required certifications and continuing education requirements with our specialized courses, designed to keep you up-to-date and equipped to handle the challenges of today's healthcare landscape.
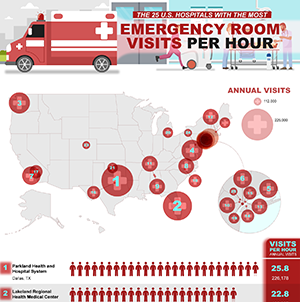
Hospitals Ranked by the Most ER Visits in the United States
|
Hospital and Location |
Annual Visits and Visits per Hour |
|
1. Parkland Health and Hospital System
Dallas, TX |
226,178
25.8 |
|
2. Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center
Lakeland, FL |
199,927
22.8 |
|
3. MultiCare Good Samaritan Hospital
Puyallup, WA |
162,390
18.54 |
|
4. Inova Fairfax Hospital
Falls Church, VA |
162,335
18.53 |
|
5. Yale New Haven Hospital
New Haven, CT |
147,385
16.8 |
|
6. NYC Health + Hospitals/Lincoln
Bronx, NY |
145,864
16.6 |
|
7. Los Angeles General Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA |
143,580
16.4 |
|
8. WakeMed Raleigh Campus Raleigh, NC |
137,402
15.7 |
|
9. Grady Memorial Hospital
Atlanta, Georgia |
135,000
15.1 |
|
10. Hackensack University Medical Center
Hackensack, NJ |
133,190
15.2 |
|
11. Wellstar Kennestone Regional Medical Center
Marietta, GA |
132,984 15.1 |
|
12. Boston Medical Center
Boston, MA |
131,638
15 |
|
13. Montefiore Medical Center-Moses Campus
New York, NY |
131,092
14.9 |
|
14. NYC Health + Hospitals/Elmhurst
Queens, NY |
127,254
14.52 |
|
15. BronxCare Health System
Bronx, NY |
127,073
14.5 |
|
16. John Peter Smith Hospital
Fort Worth, TX |
125,812
14.3 |
|
17. Antelope Valley Medical Center
Lancaster, CA |
125,000
14.2 |
|
18. Cape Fear Valley Medical Center
Fayetteville, NC |
124,238
14.1 |
|
19. NYC Health + Hospitals/Kings County
Brooklyn, NY |
121,506
13.8 |
|
20. Beaumont Hospital
Royal Oak, Michigan |
119,812
13.6 |
|
21. SSM Health St. Anthony Hospital
Oklahoma City, OK |
117,678
13.4 |
|
22. Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston, MA |
117,255
13.38 |
|
23. UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital
Aurora, CO |
114,405
13 |
|
24. Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health
Lancaster, PA |
113,244
12.9 |
|
25. St. Joseph's University Medical Center
Paterson, NJ |
112,690
12.8 |
Source:
Becker’s Hospital Review (https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/rankings-and-ratings/hospitals-with-the-most-ed-visits-in-2022.html)