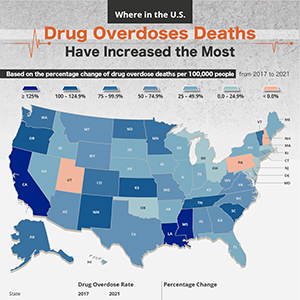
Drug overdose deaths are an epidemic in the United States. In 2021, more than 106,000 Americans died from a drug-involved overdose, and more than 75% of these deaths involved opioid drugs. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the rate of drug overdose deaths overall in the United States increased by 14% between 2020 and 2021. While the United States as a whole is seeing an increase of drug overdose deaths, some states' death rates are rising more quickly than others.
The NYRequirements.com team examined data from the CDC through the years to determine which U.S. states have seen the biggest increase in drug overdose deaths through the years. See which states' drug-related deaths have increased the most between 2017 and 2021.
Click here to download the printable PDF version of the chart.
Which States Have Seen the Biggest Increase in Drug Overdose Deaths?
Based on the data from the CDC, the state that has seen the biggest increase in drug-related deaths between 2017-2021 is Mississippi. The Magnolia State saw a 132.79% increase in drug overdose deaths between the years of 2017 and 2021. In 2017, Mississippi had an overdose death rate of 12.2 per 100,000 people, and in 2021 that rate went up to 28.4 per 100,000 people.
The state with the second-highest increase in drug-involved deaths is Louisiana. The state had an overdose death increase of 128.16% between 2017 (24.5 per 100,000) and 2021 (55.9 per 100,000).
These are the ten states with the biggest increase in drug overdose deaths between 2017 and 2021:
- Mississippi: 132.79% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- Louisiana: 128.16 % increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- California: 127.35% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- Oregon: 116.13% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- Tennessee: 112.78% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- South Carolina: 108.78% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- New Mexico: 108.06% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- Kansas: 105.93% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- North Dakota: 86.96% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
- Washington: 84.87% increase in deaths per 100,000 people
There were three states that saw a decrease in drug-related overdose deaths between the same period. The state with the biggest decrease was New Hampshire at -12.70%, followed by Utah (-5.38%) and Pennsylvania (-2.48%). In 2019, New Hampshire launched a three-year Action Plan with the goal of tackling the state's alcohol and drug addiction crisis. The program has overall been successful, with drug overdose deaths decreasing significantly since 2017.
The Opioid Epidemic
Since 1999, more than 1 million Americans have died due to a drug overdose. What is the most dangerous drug available? Currently, opioids are the most dangerous in terms of drug overdose deaths. They are highly addictive and users can build up a tolerance, which over time requires a higher dose to achieve the same effect. While heroin is one of the most well-known opioids, there are many prescription opioid drugs that are also abused. Some of the most common prescription opioids available are oxycodone (Oxycontin), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and fentanyl. Depending on the state, many different types of healthcare professionals are required to take courses to prescribe controlled substances for patients.
The fentanyl overdose death epidemic has been increasingly troubling in the United States. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid drug that was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. It is very similar to morphine, but is 50 to 100 times more potent. It is typically given to patients experiencing extreme pain, especially after surgery. Because it is so potent, it poses a high risk of overdose.
Some of the effects of fentanyl include:
- happiness
- sedation
- drowsiness
- confusion
- nausea
- problems breathing
Some drug dealers will mix cheap fentanyl into other drugs like cocaine and heroin in order to produce a cheaper high for their customers, thus increasing their profits. Unfortunately, because users don't know how much fentanyl their products contain, deaths from fentanyl can be common.
According to the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, in 2023 alone, law enforcement in the United States seized more than 360 million deadly doses of fentanyl. Despite the government's spending of $40 billion dollars on the drug war, fentanyl still remains cheap and widely available on the streets.
U.S. States With the Most Overall Drug Overdose Deaths
In 2021 (the most recently available data from the CDC), the following states had the highest total drug-related deaths:
- California: 10,901 deaths
- Florida: 7,827 deaths
- New York: 5,842 deaths
- Pennsylvania: 5,449 deaths
- Ohio: 5,397 deaths
- Texas: 4,984 deaths
- North Carolina: 3,981 deaths
- Tennessee: 3,813 deaths
- Illinois: 3,762 deaths
- Michigan: 3,089 deaths
U.S. States With the Biggest Increases in Drug Overdose Deaths
| Rank | State | Deaths Per 100,000 (2017) | Deaths Per 100,000 (2021) | Percent Change |
| 1 |
Mississippi |
12.2 | 28.4 | 132.79 |
| 2 |
Louisiana |
24.5 | 55.9 | 128.16 |
| 3 |
California |
11.7 | 26.6 | 127.35 |
| 4 |
Oregon |
12.4 | 26.8 | 116.13 |
| 5 |
Tennessee |
26.6 | 56.6 | 112.78 |
| 6 |
South Carolina |
20.5 | 42.8 | 108.78 |
| 7 |
New Mexico |
24.8 | 51.6 | 108.06 |
| 8 |
Kansas |
11.8 | 24.3 | 105.93 |
| 9 |
North Dakota |
9.2 | 17.2 | 86.96 |
| 10 |
Washington |
15.2 | 28.1 | 84.87 |
| 11 |
Minnesota |
13.3 | 24.5 | 84.21 |
| 12 |
Vermont |
23.2 | 42.3 | 82.33 |
| 13 |
Colorado |
17.6 | 31.4 | 78.41 |
| 14 |
Alaska |
20.2 | 35.6 | 76.24 |
| 15 |
Arizona |
22.2 | 38.7 | 74.32 |
| 16 |
Virginia |
17.9 | 30.5 | 70.39 |
| 17 |
Alabama |
18 | 30.1 | 67.22 |
| 18 |
Montana |
11.7 | 19.5 | 66.67 |
| 19 |
North Carolina |
24.1 | 39.2 | 62.66 |
| 20 |
Texas |
10.5 | 16.8 | 60 |
| 21 |
Georgia |
14.7 | 23.5 | 59.86 |
| 22 |
West Virginia |
57.8 | 90.9 | 57.27 |
| 23 |
Missouri |
23.4 | 36.5 | 55.98 |
| 24 |
Wyoming |
12.2 | 18.9 | 54.92 |
| 25 |
Kentucky |
37.2 | 55.6 | 49.46 |
| 26 |
Florida |
25.1 | 37.5 | 49.4 |
| 27 |
Wisconsin |
21.2 | 31.6 | 49.06 |
| 28 |
South Dakota |
8.5 | 12.6 | 48.24 |
| 29 |
New York |
19.4 | 28.7 | 47.94 |
| 30 |
Indiana |
29.4 | 43 | 46.26 |
| 31 |
Delaware |
37 | 54 | 45.95 |
| 32 |
Arkansas |
15.5 | 22.3 | 43.87 |
| 33 |
Nebraska |
8.1 | 11.4 | 40.74 |
| 34 |
Maine |
34.4 | 47.1 | 36.92 |
| 35 |
Connecticut |
30.9 | 42.3 | 36.89 |
| 36 |
Nevada |
21.6 | 29.2 | 35.19 |
| 37 |
Rhode Island |
31 | 41.7 | 34.52 |
| 38 |
Illinois |
21.6 | 29 | 34.26 |
| 39 |
Iowa |
11.5 | 15.3 | 33.04 |
| 40 |
Idaho |
14.4 | 19 | 31.94 |
| 41 |
Hawaii |
13.8 | 17.3 | 25.36 |
| 42 |
Oklahoma |
20.1 | 24.4 | 21.39 |
| 43 |
Maryland |
36.3 | 42.8 | 17.91 |
| 44 |
Massachusetts |
31.8 | 36.8 | 15.72 |
| 45 |
Michigan |
27.8 | 31.5 | 13.31 |
| 46 |
New Jersey |
30 | 32.4 | 8 |
| 47 |
Ohio |
46.3 | 48.1 | 3.89 |
| 48 |
Pennsylvania |
44.3 | 43.2 | -2.48 |
| 49 |
Utah |
22.3 | 21.1 | -5.38 |
| 50 |
New Hampshire |
37 | 32.3 | -12.7 |